Malignant melanoma is the most aggressive type of skin cancer, with the highest rates of metastasis and mortality. The incidence of metastatic melanoma has increased over the past 3 decades, with a mortality rate that continues to rise more quickly than that of most other cancers. N-(2-(dimethylamino)ethyl)-5-[18F]fluoropicolinamide ([18F]DMPY2) is 18F-labeled pyridine-based benzamide derivative with a dimethylamine residue. The skeleton structure (benzamide) has a selective affinity for the pigment melanin, which is an irregular polymer produced by melanocytes. [18F]DMPY2 showed excellent performance in detecting melanoma. The specific/rapid targeting, prolonged retention, and rapid clearance of [18F]DMPY2 in primary and metastatic tumors suggest that this radiotracer could be used as a PET imaging agent to obtain outstanding image quality in the diagnosis of melanoma.
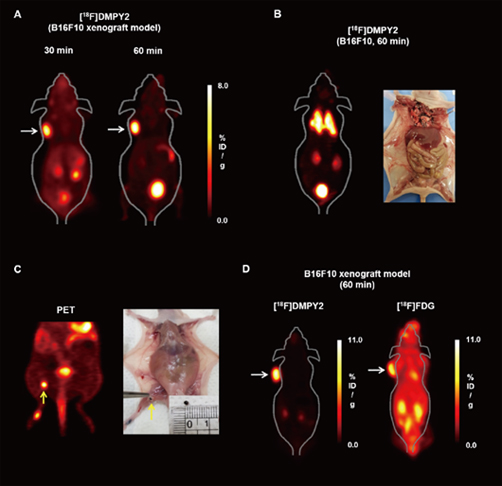
(A) Tumor xenograft models.
(B) Lung metastasis mouse models.
(C) Lymph node metastasis mouse models.
(D) Coronal images of B16F10 bearing mice models at 60 min post-injection of [18F]DMPY2 (left) and [18F]FDG (right).